Sending a Transaction
Authentification
The API-Key-Secret is sent as header in X-API-Key and authorizes the request.
Bring Your Own Private Key
Optionally, a private key can be passed in the headers using X-Private-Key. This private key is used to sign the transaction instead of the default identity assigned to the API key.
Transaction Request
Transactions can be provided in different formats, with a focus on human-friendly interactions.
The OpenAPI Documentation for the Endpoint is available here:
https://app.vechain.energy/docs/api/transact (opens in a new tab)
A transaction can be tested in the API documentation, and with the help of the Contract Manager, code snippets can also be generated.
Simplified String
<address>.<funcName>(...[type value])For example:
0x8384738C995D49C5b692560ae688fc8b51af1059.increment()Values with , can be escape with a \, for example: .funcName(string 1\\,5).
ABI
If an ABI definition is given, the function call is encoded using the ABI definition and the list of args.
{
"to": "0x8384738C995D49C5b692560ae688fc8b51af1059",
"abi": {
"inputs": [],
"name": "increment",
"outputs": [],
"stateMutability": "nonpayable",
"type": "function"
},
"args": []
}Signatures
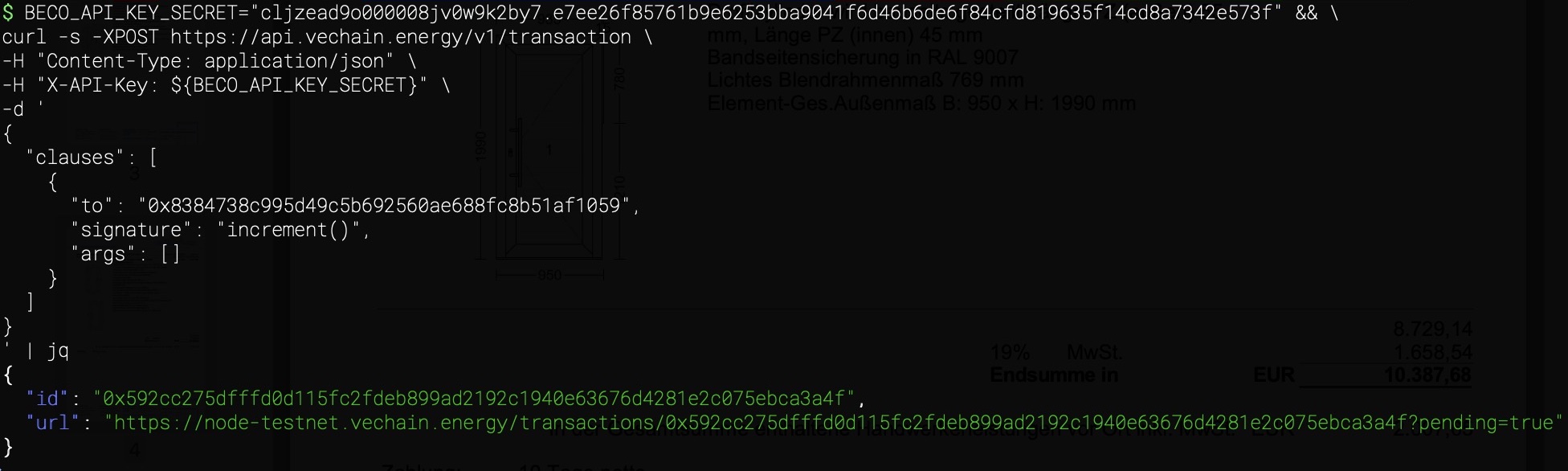
Using a signature is simpler than an ABI, it is the function definition with data types and more human friendly:
{
"to": "0x8384738C995D49C5b692560ae688fc8b51af1059",
"signature": "increment()",
"args": []
}Raw Clause Data
Already encoded data can be sent as raw clause data:
{
"to": "0x8384738C995D49C5b692560ae688fc8b51af1059",
"data": "0xd09de08a"
}Contract-Deployments can be achieved sending data without to.